CASE STUDY
Combining the power of AI with the modern Utsira OBN survey
This case study is an example of artificial intelligence (AI) geological interpretation applied to a large-scale, densely sampled ocean bottom node (OBN) seismic dataset, Utsira OBN, in the Norwegian north Sea. The resulting suite of derivative seismic interpretation products provides enhanced insights in an area where infrastructure led exploration is being pursued by the E&P industry.

Efficiently and accurately create derivative seismic interpretation products based on the Utsira OBN survey
1,500 square kilometers
The Norwegian North Sea
Geological interpretation of the world's largest OBN survey
The aim of this project was to perform geological interpretation on the large-scale, densely sampled Utsira OBN survey covering over 1,500 square kilometres.
AI-assisted geoscience software for interpretation of wells and seismic
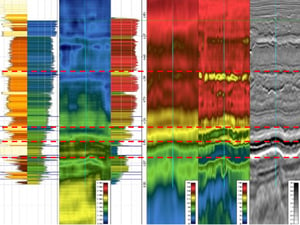
Predicting missing well logs, and rock- and fluid property curves, interpreting faults and geobodies through automatic seismic interpretation, and producing 3D property volumes of lithology, porosity, density and Vp velocity.

“The collaboration with Earth Science Analytics is an opportunity for TGS to maximize extraction of the subsurface data insights within our energy data library with integrated, AI-powered workflows. Application of these workflows on our Utsira OBN dataset has already produced startling results, and we look forward to future successes.”
A set of data-driven geological insights, property predictions, and structural attributes
AI methods were applied in an integrated approach to de-risking sand presence and fluid type in the Utsira High area. Injectite and fault interpretation using EarthNET proved to be robust and efficient, yielding accurate models for improved understanding of migration pathways, compartmentalisation, and reservoir presence. 3D property predictions of Vp and density using AI-models trained locally on wells and the OBN dataset show high accuracy when compared against test wells and an available FWI velocity model. Strong capabilities of de-risking Eocene channel sands have been demonstrated by benchmarking the results against a blind test well and the FWI velocity model.

Provided a unique, previously unseen insight into the prospectivity of this region
Interpretation cycle time was drastically reduced from years to months through the use of the AI-assisted interpretation modules in EarthNET.
By using AI models trained on vast amounts of QC'ed data, human bias and subjectivity is reduced and the accuracy of the interpretation increased.